Newly published research by Canadian scientists show a rapidly warming southern Antarctic Ocean. Melting ice and increasing rainfall are also contributing to decreasing salinity, or “freshening” of the southern ocean
Neil Swart (PhD) research scientist from Environment and Climate Change Canada led the team.
ListenWhat they discovered was the relation between greenhouse gas influence, along with ozone depletion’s influence
The research was published in the science journal, “Nature Geoscience” under the title, “Recent Southern Ocean warming and freshening driven by greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion” (abstract HERE)
The researchers found that the southern ocean is warming at twice the rate of global oceans beyond any natural influence and due to what Swart says is human activity.

Neil Swart (PhD) lead author of the research paper on warming of the Antarctic ocean (supplied)

Image of an Antarctic ice shelf in 2005 . (N Swart)
They found that while the ozone depletion is indeed diminishing and thus its effect on warming, that of greenhouse gas continues to increase and outpaces any benefits from a reduced ozone hole.
The scientists note that the southern ocean absorbs a major proportion of CO2 as currents sink to the deep ocean bottom.

Members of the research team hold an “Argo float”, an autonomous scientific device dropped into the ocean where it sinks to 2000 m, waits 10 days and rises up the surface measuring temperature and salinity along the way, and then sending the data back via satellite, and repeats. A significant amount of data in the study came from Argo floats (N Swart).
Those warmer currents however, rise back to the surface thousands of kilometres away and because they are warmer, begin to affect the climate and marine life far from Antarctica.

The Canadian research team determined that ocean warming and freshening around Antarctica was far beyond any “natural” change and was caused by human activity adding greenhouse gas to the atmosphere, and depleting the ozone layer, (N Swart)
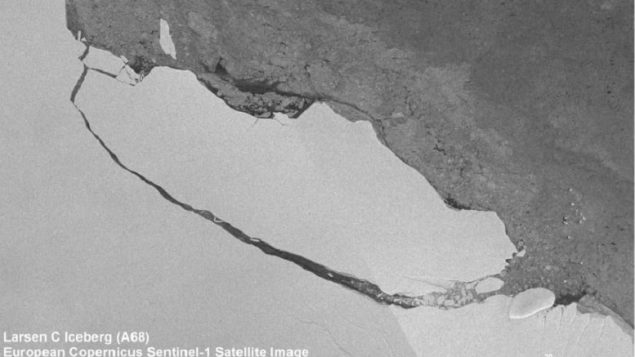
This warming while contributing to ocean rise is also a cause for concern in the melting and breaking off of giant Antarctic ice sheets, which as they melt also add to both ocean rise and freshening of the ocean.
Swart says the findings add to the knowledge of the relationship of greenhouse effects, ocean currents and will help create even more accurate climate modelling.






For reasons beyond our control, and for an undetermined period of time, our comment section is now closed. However, our social networks remain open to your contributions.